
What is Broadband?
Broadband is the transmission of high-quality data of wide bandwidth. In its simplest form, it is high-speed internet access that is always on and faster than the traditional dial-up access. Broadband includes several high-speed transmission technologies such as: fiber optics, wireless, cable, DSL and satellite.
Comparing Types of Technology
- Fiber: Uses ultra-thin glass strands that carry light instead of electricity. Since light can travel very quickly through fiber-optic cables, fiber connection can see gigabit speeds 100x faster than DSL. Additionally, fiber allows for symmetrical speeds, which means you have fast upload speeds that match your download speeds. A single fiber can carry multiple streams of information at the same time, which enables more robust video, internet, and voice services.
- Cable: Cable modems allow for data transmission on the same coaxial cables used by cable companies to send video and audio to your television.
- Fixed Wireless: A wireless broadband internet connection uses a radio link to connect your devices – via an antenna – to a service provider’s facility and then to the internet. The antenna needs to have "line of sight" to the service providers facility to be effective.
- 5G Home Internet (Cellular): Mobile internet, which is mostly designed for your phone, sends 5G (5th Generation Mobile Network) signals in all directions. Most of these signals are picked up by cell phones, but in the case of home internet, a router receives these signals and turns them into a home connection. Additionally, some cellular internet plans use LTE, the previous generation of technology, or a mix of LTE and 5G.
- Satellite: A form of wireless broadband, but uses satellites in the Earth's orbit to transmit data. This connection requires line-of-sight to the satellite and can be negatively affected by weather. Satellite speeds are slower than DSL and Cable. Service requires a dish antenna and can be quite expensive compared to other types of connections.
To learn more about the pros and cons of each technology type visit our FAQ page.
How Much Speed is Enough?
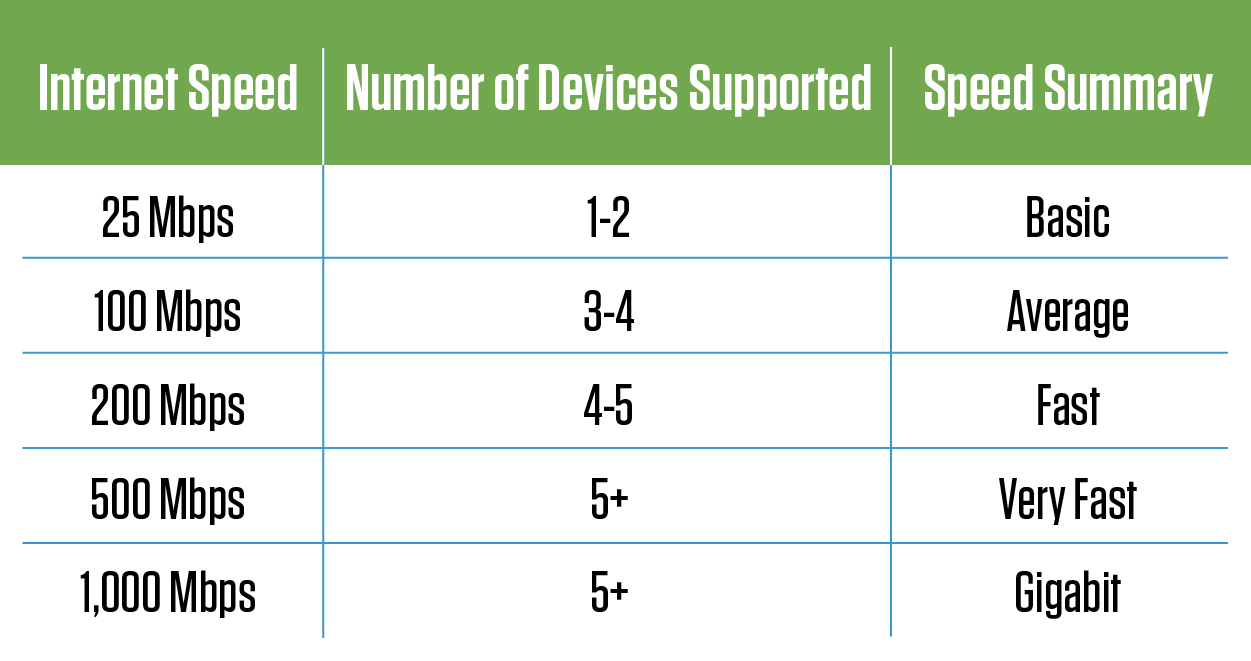
Calculators such as this one at BroadbandNow can help you quantify the amount of speed you need.
Why Fiber is the Best Choice

- It’s the fastest.
- It’s symmetrical.
- It’s dedicated.
- It’s future-proof and sustainable.
- It’s a better investment.
- It’s reliable.
- It amplifies economic development.
Fiber Communities are Empowered Communities
Fiber-to-the-home communities are the centers of innovation that are worth visiting, working in, and living in. Fiber delivers the best broadband for:
 Education Education
Teleworking
Telehealth
Economic Development
Precision Agriculture
To connect with a ICA provider offering fiber, please click here to access a searchable map, showing the towns served by ICA's community-based telecommunications provider members.

Broadband Resources
For a list of broadband resources visit this page to find links to state and federal broadband maps, state and federal funding programs, and industry resources.
FAQ
Visit our frequently asked questions page to learn more about how to connect your community, find an ICA member provider, and gain more insight into the differences in technology types.
|